Coblator Assisted Adeno Tonsillectomy
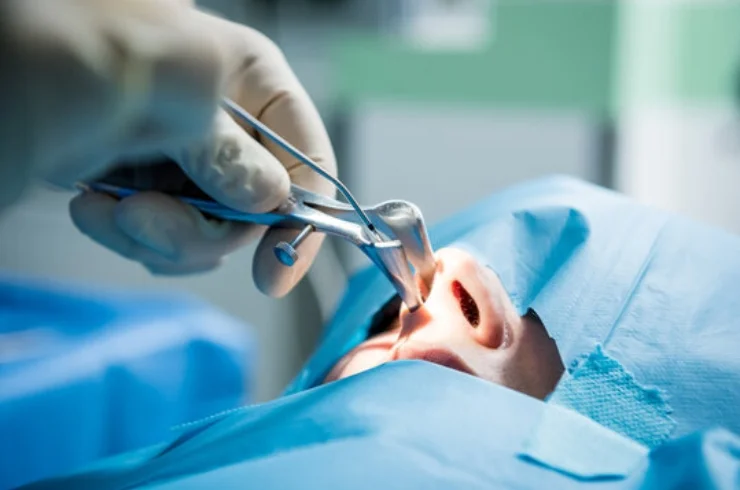
Coblator Assisted Adenotonsillectomy is a modern surgical technique used for the removal of the tonsils and adenoids, which are often required due to chronic infections, obstructive sleep apnea, or other related conditions. The procedure utilizes a specialized device called the coblator, which employs radiofrequency energy to remove tissue with minimal heat. This technology helps reduce pain, bleeding, and recovery time compared to traditional methods.
What is Coblation?
Coblation (Controlled Ablation) is a process that uses radiofrequency energy and a conductive solution, such as saline, to generate a low-temperature plasma field. This field is capable of precisely removing or vaporizing soft tissue without causing excessive thermal damage to surrounding areas. Unlike traditional methods like cauterization or laser surgery, coblation operates at much lower temperatures, making it a more gentle and effective choice for delicate procedures like adeno-tonsillectomies.
Indications for Coblator Assisted Adenotonsillectomy
The procedure is commonly performed for the following conditions:
- Chronic Tonsillitis: Recurrent infections of the tonsils that do not respond to antibiotics.
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): Tonsils and adenoids that block the airway during sleep, leading to breathing problems.
- Hypertrophic Tonsils: Enlarged tonsils that cause difficulty in swallowing or breathing.
- Snoring: Excessive snoring due to enlarged tonsils or adenoids.
- Peritonsillar Abscess: A painful collection of pus near the tonsils.
Procedure Overview
Preparation: The patient is typically placed under general anesthesia for the surgery, ensuring they are fully relaxed and unaware of the procedure.
Use of Coblator: The surgeon uses the coblator device, which is inserted through the mouth to reach the tonsils and adenoids. The device emits radiofrequency energy to gently remove the tissue by turning it into a gaseous state with minimal heat. This method avoids the high temperatures associated with traditional electrocautery.
Tissue Removal: The coblator assists in the precise removal of the tonsils and/or adenoids. It also helps seal the blood vessels, reducing bleeding during the procedure.
Post-Surgery Care: Once the tonsils and adenoids are removed, the patient is monitored in the recovery room. Most patients can go home the same day, although some may require an overnight stay, depending on the complexity of the procedure.
Advantages of Coblator Assisted Adenotonsillectomy
- Minimally Invasive: The coblation technology provides a precise and controlled approach to tissue removal with less collateral damage to surrounding structures.
- Reduced Pain: Compared to traditional methods, coblation is associated with less postoperative pain due to lower temperatures used during tissue removal.
- Minimal Bleeding: The coblator helps coagulate blood vessels during surgery, significantly reducing the risk of bleeding, a common concern with traditional tonsillectomy methods.
- Faster Recovery: With less trauma to the tissues, patients typically experience a faster recovery time, often returning to normal activities sooner than with conventional surgery.
- Shorter Hospital Stay: In most cases, coblator-assisted adeno-tonsillectomy can be performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to go home the same day.
Risks and Complications
While the procedure is generally safe, like any surgery, there are potential risks:
- Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a small risk of infection at the surgical site.
- Bleeding: Though the coblator helps minimize bleeding, there is still a slight risk of postoperative bleeding.
- Pain: Some discomfort or pain is typical after the procedure, but it is generally milder than traditional methods.
- Delayed Healing: While coblation leads to quicker recovery, some individuals may experience delayed healing due to factors like age, underlying health conditions, or the extent of the surgery.
Postoperative Care
- Pain Management: Pain after coblator-assisted adenotonsillectomy is usually mild and managed with over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribed medication.
- Dietary Restrictions: A soft, cool diet is recommended for the first few days to avoid irritating the surgical site.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is crucial for healing and preventing complications like dehydration or dry throat.
- Follow-up: A follow-up appointment is typically scheduled within a week to monitor healing and ensure no complications have arisen.
